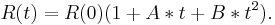Callendar–Van Dusen equation
The Callendar–Van Dusen equation is an equation that describes the relationship between resistance (R) and temperature (t) of platinum resistance thermometers.
It is also used in the international standard DIN EN 60 751 (IEC751). For a more accurate relationship, the ITS-90 is used.
For the range between -200 °C to 0 °C the equation is
For the range between 0 °C to 661 °C the equation is
These equations are listed as the basis for the temperature/resistance tables for platinum resistance thermometers and are not intended to be used for the calibration of individual thermometers.
The coefficients for individual thermometers (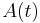 and
and 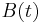 ) can be obtained by calibration.
) can be obtained by calibration.
The equation was found by British physicist Hugh Longbourne Callendar, and refined by M. S. Van Dusen.
![R(t) = R(0) [ 1 %2B A*t %2B B*t^2 %2B (t - 100)C*t^3].](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/40bc12627391235392ce874d08612b0e.png)